Products Description
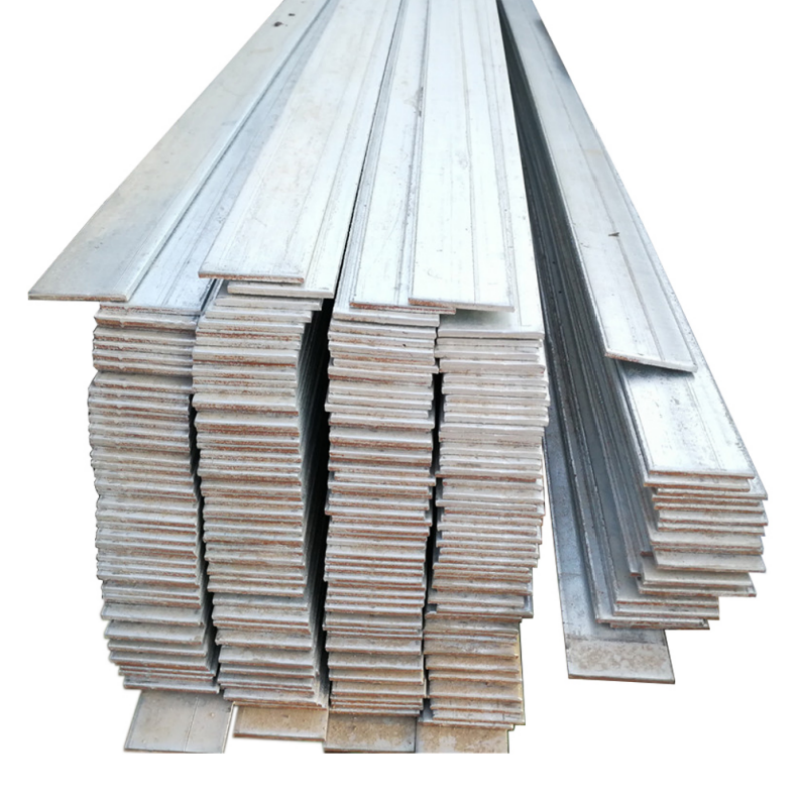
| Product Name | Flat bar |
| Standard | ASTM, BS, GB, JIS, etc. |
| Grade | SS400, ST37-2, A36, S235JRG1, Q235, Q345, etc. |
| Technique | Hot Rolled |
| Thickness | 2.0mm-24mm |
| Size | 20mm-200mm |
| Usage | Widely used in various building structure and engineering structure |
| Delivery Time | 10-20days |
| Shipping | 1.Shipping by containers 2.Shipping by bulk ship |
Galvanized flat steel is a type of flat steel that has been galvanized and covered with a layer of zinc to improve its corrosion resistance and service life.
1. Basic features
Material: usually made of high-quality carbon structural steel (such as Q235), which is formed by hot rolling or cold rolling and then galvanized.
Galvanizing method: There are two common galvanizing methods: hot-dip galvanizing and electro-galvanizing. Hot-dip galvanizing is to immerse flat steel in molten zinc liquid to form a dense zinc layer on the surface of the steel through chemical reaction; electro-galvanizing is to deposit a zinc layer on the surface of the steel through electrolysis.
Cross-sectional shape: flat, the width and thickness can be customized according to needs, the common width ranges from a few millimeters to hundreds of millimeters, and the thickness ranges from a few millimeters to tens of millimeters.
2. Advantages
Strong corrosion resistance: The galvanized layer can effectively isolate the steel from direct contact with corrosive media such as air and water, significantly improving the corrosion resistance of the steel.
Long service life: Due to the protective effect of the galvanized layer, the service life of galvanized flat steel is much longer than that of ungalvanized steel.
High aesthetics: The galvanized layer has a smooth surface and uniform color, which can improve the overall aesthetics of the product.
Good processing performance: Galvanized flat steel is easy to cut, weld, drill and other processing operations, and is convenient for on-site installation and construction.
3. Application areas
Construction field: used to make steel structure frames, supporting components, railings, handrails, etc., and as grounding wires for electrical equipment.
Transportation field: used to make highway guardrails, bridge components, railway track fixings, etc.
Electric power field: used as support components and connectors for power facilities such as transmission towers and substations.
Communication field: used to make support structures for communication towers, antenna brackets and other communication facilities.
Other fields: It is also widely used in chemical industry, petroleum, shipbuilding, machinery manufacturing and other industries.
OUR ADVANTAGE
 10+ YEARS EXPORT
10+ YEARS EXPORT QUALITY CERTIFICATES
QUALITY CERTIFICATES SERVICE FIRST
SERVICE FIRST INNOVATIVE DEVELOPMENT
INNOVATIVE DEVELOPMENT INNOVATION LEADS
INNOVATION LEADS EXPORT VOLUME
EXPORT VOLUME






 WhatsApp
WhatsApp E-mial
E-mial